Astigmatism is a common eye condition where the shape of the cornea or the lens is not perfectly round, causing blurred or distorted vision. It is estimated to affect around one in three people in the United States, and while it can be corrected with eyeglasses or contact lenses, it can also have long-term implications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, diagnosis, risk factors, long-term implications, prevention, treatment options, and answer the question “can LASIK fix astigmatism”.
Astigmatism Symptoms
The main symptom of astigmatism is blurred or distorted vision, both at distance and up close. This can cause difficulty in reading, driving, or seeing details in objects. In addition, people with astigmatism may experience headaches, eyestrain, and fatigue, particularly after extended periods of reading or screen use.
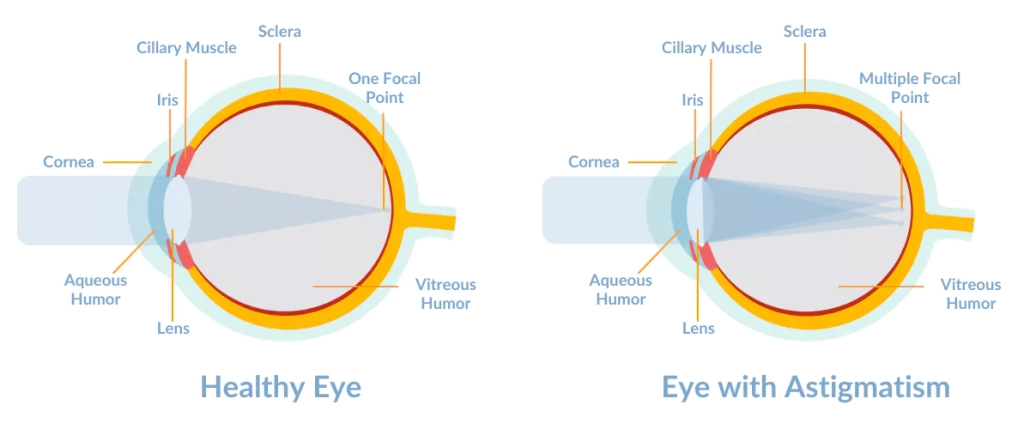
Diagnosing Astigmatism
Astigmatism can be diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam, which may include a visual acuity test, a refraction test, and a keratometry test. The refraction test measures the degree of refractive error, while the keratometry test measures the curvature of the cornea.
Early Detection of Astigmatism
Early detection of astigmatism is important to prevent further vision problems. Children should have their eyes checked regularly, particularly before starting school. Adults should have their eyes checked at least once every two years, or more frequently if they have a family history of eye problems or other risk factors.
Risk Factors Associated with Astigmatism
The exact causes of astigmatism are not known, but certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing the condition. These include genetics, eye injuries, and conditions such as keratoconus and cataracts.
Long Term Implications of Astigmatism
If left untreated, astigmatism can cause permanent vision problems, including amblyopia (lazy eye) and strabismus (crossed eyes). In addition, it can lead to headaches, eyestrain, and fatigue, which can affect quality of life and productivity.
Astigmatism Prevention
There is no known way to prevent astigmatism, but maintaining good eye health and preventing eye injuries can help reduce the risk. This includes wearing protective eyewear during sports and other activities, taking regular breaks from screen use, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Astigmatism Treatment Options
Astigmatism can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery. Eyeglasses and contact lenses work by correcting the refractive error, while refractive surgery reshapes the cornea to correct the astigmatism. Refractive surgery includes procedures such as LASIK, PRK, and LASEK, which use lasers to reshape the cornea. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the astigmatism, the individual’s lifestyle and preferences, and their overall eye health.
LASIK and Astigmatism
Can LASIK fix astigmatism? LASIK is a popular and effective option for correcting astigmatism. During the LASIK procedure, a laser is used to reshape the cornea, correcting the refractive error and improving vision. LASIK is a quick and painless procedure, with most patients experiencing improved vision within a few days. However, LASIK is not suitable for everyone, and a comprehensive eye exam and consultation with a qualified eye surgeon is necessary to determine if LASIK is the right option.
In conclusion, astigmatism is a common eye condition that can cause blurred or distorted vision and other vision problems. Early detection, prevention, and treatment are important to prevent long-term complications and improve quality of life. LASIK is a popular and effective option for correcting astigmatism, but a comprehensive eye exam and consultation with a qualified eye surgeon is necessary to determine if LASIK is the right option for an individual’s unique needs and circumstances.